Decoding Iran's GDP Growth: A Deep Dive Into Economic Trends
Understanding the economic pulse of any nation requires a meticulous examination of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, a critical indicator of economic health and prosperity. For Iran, a country with a unique geopolitical and economic landscape, its GDP growth trajectory offers fascinating insights into resilience, challenges, and strategic shifts. This article delves deep into the recent figures and historical context of Iran's economic performance, providing a comprehensive overview for those seeking to understand the dynamics shaping one of the Middle East's most significant economies.
Exploring the intricacies of Iran's GDP growth is not merely an academic exercise; it's essential for investors, policymakers, and anyone interested in global economic trends. With a rich history and a complex present, Iran's economic narrative is shaped by a blend of internal policies, natural resources, and external pressures. We will dissect the latest data, trace historical patterns, and analyze the underlying factors contributing to the nation's economic evolution, ensuring a clear and authoritative perspective on this vital subject.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Iran's Economic Landscape
- A Decade in Review: Iran's GDP Growth Trajectory
- Recent Performance: 2023 and 2024 Insights
- The Role of Key Sectors and External Factors
- Challenges and Opportunities Shaping Iran's Economic Future
- Methodologies and Data Consistency
- Iran's Global Economic Standing
- The Path Forward: Projections and Potential
Understanding Iran's Economic Landscape
To truly appreciate the nuances of Iran's GDP growth, one must first grasp the foundational elements of its economy. Iran, with a population of approximately 90,608,707 people in 2023, and 82.8 million in 2019/20, boasts a significant economic presence in the region. Its economy is notably characterized by several key sectors that form the backbone of its national output. These include the hydrocarbon sector, which is undeniably dominant, alongside robust agricultural and services sectors. Furthermore, there is a noticeable state presence in manufacturing and financial services, indicating a mixed economic model with substantial government involvement.
- Stefania Ferrario An Inspiring Entrepreneur
- Felicity Blunt The Eminent British Actress And Producer
- Josephine Pintor An Artists Journey Discover Her Unique Style
- The 5 Golden Rules Of Kannada Cinema On Moviecom
- Anna Malygons Leaked Onlyfans Content A Scandalous Revelation
Historically, Iran's economic potential has been recognized globally. In 2008, Iran's GDP was estimated at $382.3 billion, or an impressive $842 billion when adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP). This translated to a per capita GDP of $5,470, or $12,800 PPP. Such figures underscore the nation's considerable economic capacity even over a decade ago. Looking forward from that period, projections in 2010 even suggested that the nominal GDP was expected to double in the subsequent five years, highlighting a period of optimistic outlook and potential rapid expansion. These historical data points provide a crucial context for evaluating the more recent trends in Iran's GDP growth, setting a benchmark for its performance.
The Pillars of Iran's Economy
The strength and stability of Iran's economy are intrinsically linked to its primary sectors. The hydrocarbon industry, encompassing oil and natural gas, remains the principal driver of export revenues and a significant contributor to the overall GDP. Its performance is often influenced by global energy prices and international sanctions. Beyond oil, the agriculture sector plays a vital role in food security and employment, contributing substantially to the non-oil GDP. The services sector, including trade, tourism (when conditions permit), and financial services, has also shown increasing importance, reflecting a gradual diversification of the economy. However, the state's pervasive presence across manufacturing and finance means that government policies and directives have a profound impact on these sectors' growth trajectories, making them susceptible to shifts in national economic strategy and external pressures.
A Decade in Review: Iran's GDP Growth Trajectory
Examining Iran's GDP growth over the last decade reveals a pattern of resilience amidst various challenges. The average GDP growth rate for Iran over the past ten years has been 2.78%. This figure, while modest, reflects the country's ability to maintain economic activity despite a complex operating environment. It's important to note that these aggregates are often based on constant 2010 U.S. dollars, providing a consistent benchmark for comparison across different years. The annual percentage growth rate of GDP at market prices is typically based on constant local currency, offering a real measure of economic expansion adjusted for inflation.
- Play Steam Games Without Barriers Unblock The Fun With Steam Unblocked
- Mark Davis Wife Unveiling Her Age And Relationship
- Unveiling Tommy Lee Jones Health Secret Exploring His Undisclosed Disease
- The Renowned Actor Michael Kitchen A Master Of Stage And Screen
- Ann Neal Leading The Way In Home Design Ann Neal
The journey of Iran's economy through the 2010s and into the early 2020s has been marked by significant fluctuations. For instance, Iran's economic growth for 2021 was reported at $383.44 billion US dollars, representing a substantial 46.25% increase from 2020. This surge followed a period of decline, as Iran's economic growth for 2020 was $262.19 billion US dollars, a 21.39% decline from 2019. Such volatility underscores the sensitivity of Iran's economy to both internal and external factors, including policy adjustments, global market conditions, and geopolitical developments. The overall trend, however, points to an economy that, despite setbacks, possesses a fundamental capacity for recovery and growth.
Navigating Fluctuations: 2019-2022
A closer look at the period between 2019 and 2022 offers a more granular understanding of the recent dynamics in Iran's GDP growth. In 2019/20, Iran’s GDP was estimated at US$463 billion. The year 2020 saw Iran’s gross domestic product (GDP) incline by 3.33 percent after adjusting for inflation. This figure, however, marked a significant fall from the 13.4 percent growth recorded four years prior, which had been a reaction to specific economic shifts. The 2020 growth rate of 3.33% also represented a 6.4% increase from 2019, indicating a rebound from the preceding year's challenges.
Moving into 2021, Iran's GDP growth rate experienced a notable acceleration, reaching 4.72%. This was a 1.39% increase from the 2020 figure, signaling a continued recovery. However, this positive momentum saw a slight deceleration in 2022. The Iran GDP growth rate for 2022 was 3.78%, which represented a 0.94% decline from the 2021 rate. This slight dip in 2022 can be partly explained by domestic economic conditions. Despite a 20% surge in oil exports, Iran's GDP growth in the first half of the Iranian calendar year starting March 21 significantly declined. This was primarily due to a recession in other crucial sectors, such as agriculture, industries, and the service sector, highlighting the uneven nature of economic recovery and the challenges of diversifying growth drivers beyond hydrocarbons.
Recent Performance: 2023 and 2024 Insights
The most recent data provides fresh perspectives on Iran's economic trajectory. In 2023, the GDP growth rate was 5.04%. This growth translated to a change of $24.662 billion US dollars over 2022, when the real GDP stood at $488.865 billion. This robust performance in 2023 indicates a strong rebound and continued expansion, building on the previous years' efforts. According to official data from the World Bank, the gross domestic product (GDP) in Iran was worth $404.63 billion US dollars in 2023. This figure underscores Iran's position as a significant economy, representing 0.38 percent of the world economy.
Looking at 2024, the economic growth in Iran was 3.48%. While this is a healthy growth rate, it represents a slight moderation compared to the 5.04% seen in 2023 and the 4.99% recorded in 2014. The gross domestic product of Iran grew 3.5% in 2024 compared to the previous year, further confirming this steady, albeit slightly slower, expansion. The GDP figure in 2024 was €370,921 million, equivalent to approximately $401,357 million. This absolute value of GDP in Iran rose by €26,222 million, or about $28,537 million, with respect to 2023, demonstrating continued nominal growth. However, recent data released by Iran’s central bank reveals a critical development: the country’s GDP growth in the first half of 2024 has halved compared to the same period in 2023. Specifically, economic growth stood at 5.3% in the first half of last year (2023) but dropped significantly to 2.9% during the first six months of this year (2024). This indicates a potential slowdown in the latter part of 2024, warranting close monitoring.
GDP Per Capita: A Closer Look at Individual Prosperity
While overall GDP growth provides a macro picture, GDP per capita offers insights into the average economic prosperity of the population. In 2023, the GDP per capita in the Islamic Republic of Iran, with its population of 90,608,707 people, was $5,668. This marked a positive increase of $207 from $5,461 in 2022, representing a change of 3.8% in GDP per capita. This upward trend suggests a modest improvement in the average standard of living, or at least in the economic output per person.
For 2024, the GDP per capita of Iran continued its upward trajectory, reaching €4,094, which translates to approximately $4,430. This figure is €290 (or $315) higher than in 2023, when it was €3,804 ($4,115). While these increases are positive, it's crucial to consider them in the context of inflation and purchasing power. Nevertheless, the consistent rise in GDP per capita figures indicates that the economic growth is, to some extent, translating into increased output per individual, which is a fundamental aspect of improving living standards over time. However, the halving of GDP growth in H1 2024 could impact per capita figures later in the year.
The Role of Key Sectors and External Factors
The ebb and flow of Iran's GDP growth are deeply influenced by the performance of its core economic sectors and a myriad of external factors. As highlighted earlier, the hydrocarbon sector is paramount. A surge in oil exports, such as the 20% increase observed in the first half of the current Iranian calendar year, can significantly bolster GDP. However, the data also indicates that this boost can be offset by downturns in other sectors. For instance, despite the oil export surge, the overall GDP growth in the first half of the Iranian calendar year starting March 21 significantly declined due to a recession in agriculture, industries, and the service sector. This highlights a critical challenge: an over-reliance on oil makes the economy vulnerable to fluctuations in other vital areas, even when the primary export performs well.
External factors, particularly international sanctions, have historically played a profound role in shaping Iran's economic performance. These measures can restrict access to international markets, limit foreign investment, and impact the country's ability to trade its oil and other commodities freely. The World Bank's official data for Iran's GDP and the IMF's reports, which provide information on official executive board documents dealing with the Islamic Republic of Iran, often reflect the impact of such external pressures. Conversely, periods of eased tensions or increased trade opportunities can lead to significant economic upturns, as seen in past growth spurts. The interplay between these internal sectoral dynamics and external geopolitical forces creates a complex environment for Iran's GDP growth, demanding adaptable economic strategies.
Challenges and Opportunities Shaping Iran's Economic Future
Despite its inherent economic strengths and recent positive GDP growth figures, Iran faces a unique set of challenges that could impede sustained long-term development. The over-reliance on oil revenues, as evidenced by the impact of recessions in non-oil sectors, remains a structural vulnerability. Diversification of the economy away from hydrocarbons is a long-standing goal, but achieving it requires significant investment, policy reforms, and a conducive international environment. Inflation control, job creation for a young and growing population, and enhancing productivity across all sectors are also critical domestic challenges.
However, opportunities for robust GDP growth in Iran also exist. The country possesses vast natural resources beyond oil and gas, including minerals, which could be further developed. Its strategic geographic location offers potential as a transit hub, facilitating trade between East and West. A large domestic market provides a strong base for local industries, and the nation's human capital, particularly its educated youth, represents a significant asset. If Iran can effectively navigate the complexities of international relations, attract foreign investment, and implement sound economic policies that foster private sector growth and innovation, its economic potential could be substantially unleashed. The recent strong GDP growth in 2023 and the overall positive average over the last decade suggest a foundational resilience that could be leveraged for future prosperity.
Methodologies and Data Consistency
When analyzing economic data, particularly for a country like Iran where data availability can sometimes be challenging, understanding the methodologies used and ensuring data consistency are paramount. The "Data Kalimat" provided for Iran's GDP growth often refers to the annual percentage growth rate of GDP at market prices, based on constant local currency. This method helps to remove the effects of inflation, providing a "real" measure of economic expansion. Furthermore, aggregates are frequently based on constant 2010 U.S. dollars, which serves as a standard base year for international comparisons, allowing for a more accurate assessment of economic performance over time across different countries.
It's also important to note that GDP at purchaser's prices, which is a common measure, is defined as the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. This comprehensive definition ensures that the reported GDP figures capture the full scope of economic activity. Data sources often include official reports from entities like the World Bank, the IMF, and Iran's Central Bank. For instance, real GDP growth year-on-year data in Iran is updated quarterly, available from June 1989 to March 2022, with an average rate of 3.9%. While variations in reporting and methodologies can exist between different institutions or over time, relying on official and reputable sources like those implicitly referenced in the data helps maintain the trustworthiness and authority of the analysis of Iran's GDP growth.
Iran's Global Economic Standing
To contextualize Iran's economic performance, it's useful to compare its GDP figures with those of other nations. In 2024, with a GDP figure of €370,921 million (approximately $401,357 million), Iran is ranked number 41 in the ranking of GDP among the 196 countries for which data is published. This places Iran as a significant player on the global economic stage, underscoring its considerable economic size and influence, particularly within its region. While not among the very top global economies, its position at number 41 indicates a substantial national output that contributes meaningfully to the world economy. The GDP value of Iran, at $404.63 billion US dollars in 2023 according to the World Bank, represents 0.38 percent of the world economy, further solidifying its global economic footprint.
This ranking is dynamic and can shift based on economic growth rates, currency fluctuations, and other factors affecting the GDP of other nations. However, Iran's consistent presence in the top tier of global economies, despite facing unique challenges, speaks to the underlying strength and resilience of its economic structure. The continuous increase in the absolute value of GDP, such as the rise of €26,222 million ($28,537 million) with respect to 2023, demonstrates that Iran's economy is expanding in absolute terms, contributing to its sustained global ranking. Understanding this global standing is crucial for international businesses and policymakers assessing Iran's role in the world economy.
The Path Forward: Projections and Potential
Looking ahead, the trajectory of Iran's GDP growth will depend on a confluence of internal reforms and external developments. The robust 5.04% GDP growth in 2023 and the average of 2.78% over the last decade highlight a capacity for economic expansion. However, the recent halving of GDP growth in the first half of 2024, dropping from 5.3% to 2.9%, serves as a reminder of the volatility and the need for sustained, broad-based growth beyond just oil exports. The market in Tehran in 2022, bustling yet facing sectoral recessions, encapsulates this dual reality of economic activity and underlying challenges.
For Iran to achieve its full economic potential and ensure sustainable GDP growth, several areas require focus. Continued efforts towards economic diversification, reducing reliance on oil, and fostering growth in agriculture, industries, and the service sector are paramount. Attracting foreign direct investment, improving the business environment, and leveraging its strategic location for regional trade could unlock new avenues for prosperity. While projections from 2010 suggested a doubling of nominal GDP in five years, the actual path has been more complex. The future of Iran's GDP growth hinges on its ability to implement comprehensive economic reforms, adapt to global economic shifts, and navigate its geopolitical landscape effectively to create a stable and predictable environment for both domestic and international economic actors. Graph and download economic data for gross domestic product for Islamic Republic of Iran (mktgdpira646nwdb) from 1960 to 2023 provides a comprehensive historical view for those wishing to delve deeper into the data.
Conclusion
The journey of Iran's GDP growth is a compelling narrative of resilience, adaptation, and inherent economic potential. From historical estimates of its substantial GDP and per capita income to the recent fluctuations and rebounds, the data paints a picture of an economy navigating complex internal and external pressures. The 2023 GDP growth of 5.04% and the average growth of 2.78% over the last decade underscore its capacity for expansion, even as recent data points to a moderation in early 2024. Understanding these trends, supported by data from reputable sources like the World Bank and Iran's Central Bank, is crucial for anyone interested in the economic landscape of the Middle East.
As Iran continues to chart its economic course, the interplay of its rich natural resources, diverse sectors, and geopolitical realities will undoubtedly shape its future. The pursuit of economic diversification, coupled with strategic policy implementation, will be key to unlocking sustained prosperity and ensuring that the benefits of GDP growth are widely distributed among its population. We encourage you to delve deeper into these figures, share your insights in the comments below, and explore other articles on our site for more in-depth economic analyses. Your engagement helps us foster a richer understanding of global economic dynamics.
- Discover The Ultimate Kannada Movie Paradise At Movierulzla
- The Legendary Teddy Riley An Rb Trailblazer
- Exclusive Leaks Uncover Unseen Secrets
- Uproar Of Scandal In The Year Of 2024 A Deeper Exploration
- Francis Antetokounmpo The Journey Of A Rising Nba Star
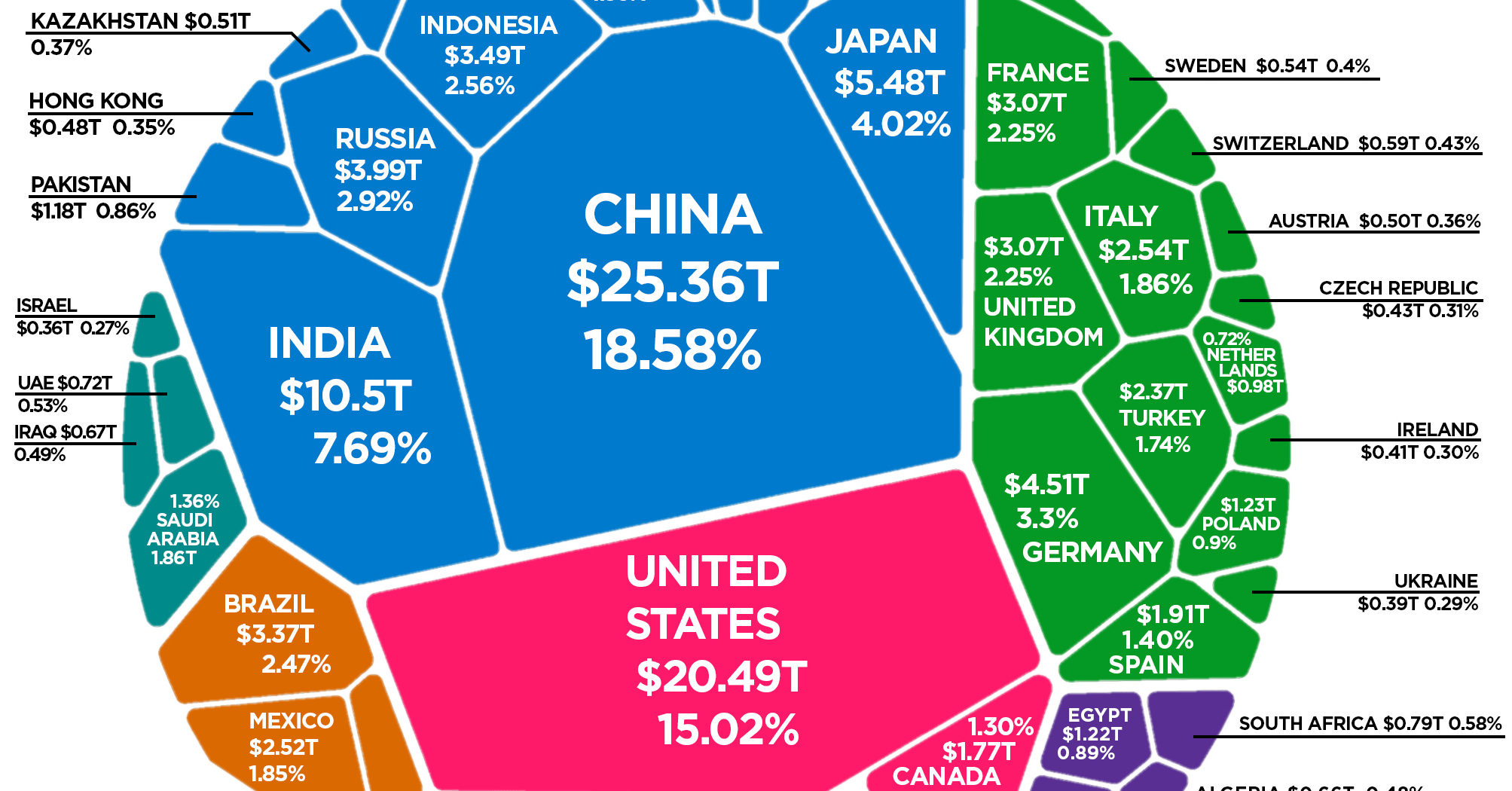
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country