Iran's GDP Per Capita: Unraveling Economic Trends
Understanding a nation's economic health often begins with a fundamental metric: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita. For Iran, this figure offers a compelling lens through which to view its complex economic journey, marked by both resilience and significant challenges. This article delves deep into Iran's GDP per capita, exploring its historical trajectory, recent fluctuations, and what these numbers truly mean for the average Iranian citizen.
From historical highs in the 1970s to the more recent impacts of global economic shifts and geopolitical pressures, Iran's GDP per capita tells a story of an economy constantly adapting. By examining the data, including nominal values and purchasing power parity (PPP), we can gain a clearer understanding of the economic realities faced by one of the Middle East's most influential nations.
Table of Contents
- Understanding GDP Per Capita: A Key Economic Indicator
- Iran GDP Per Capita: A Historical Perspective
- Recent Trends and Figures (2020-2024)
- Nominal vs. Purchasing Power Parity (PPP): A Deeper Dive
- Iran GDP Per Capita in the Global Context
- Factors Influencing Iran GDP Per Capita
- Challenges and Outlook for Iran's Economic Future
- Conclusion: Navigating Iran's Economic Landscape
Understanding GDP Per Capita: A Key Economic Indicator
Before diving into the specifics of Iran's economic performance, it's essential to grasp what GDP per capita represents. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total monetary or market value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period. It's a broad measure of a nation's overall economic activity. When we talk about **GDP per capita**, we are referring to the gross domestic product divided by the mid-year population. This calculation provides an average measure of economic output per person, offering a more nuanced understanding of living standards and economic productivity than GDP alone. It helps to normalize the economic output for population size, allowing for better comparisons between countries of different sizes. Essentially, it reflects the average income and productivity of each individual in a country. Furthermore, GDP itself is defined as the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. This comprehensive definition ensures that GDP captures the full scope of economic activity.Iran GDP Per Capita: A Historical Perspective
Iran's economic history, particularly concerning its GDP per capita, is a narrative of significant peaks and troughs, deeply influenced by geopolitical events, oil price fluctuations, and domestic policies. Data from sources like the World Bank provides a comprehensive look at this journey, tracing back to 1960.Early Trends and Record Highs
Looking back, the **GDP per capita in Iran** has seen remarkable shifts. From 1960 until 2023, the average nominal GDP per capita in Iran stood at approximately $4,435.95 USD. However, this average masks significant volatility. The historical data reveals a record low of $195.58 USD in 1960, which marked the beginning of the recorded series. Following this, Iran experienced a period of significant economic growth, largely fueled by its vast oil reserves and rising global oil prices. This growth culminated in an all-time high of $7,422.13 USD in 1976. This period represented a time of considerable prosperity and development for the nation, showcasing its potential when global and internal conditions were favorable.Fluctuations and Long-Term Averages
After the peak in the mid-1970s, Iran's GDP per capita began to experience more pronounced fluctuations. The period from 1980 to 2024 saw the GDP per capita rise by approximately $2.19 thousand USD, indicating a gradual, albeit often volatile, upward trend over several decades. Historically, the average for Iran from 1960 to 2023 is $2,659.16 USD in current US dollars. These long-term averages provide a baseline but also highlight the dynamic nature of Iran's economy, which has navigated wars, sanctions, and varying degrees of international engagement. The ability to graph and download economic data for constant GDP per capita for the Islamic Republic of Iran (NYGDPPCAPKDIRN) from 1960 to 2023 further allows economists and analysts to observe these real trends, accounting for inflation and providing a clearer picture of actual economic growth per person over time.Recent Trends and Figures (2020-2024)
The most recent years offer a snapshot of Iran's economic performance under contemporary pressures, particularly global sanctions and the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. The data reveals a mixed picture of decline, recovery, and modest growth. In 2020, Iran's GDP per capita was recorded at $2,989 USD, representing a significant 21.99% decline from 2019. Another estimate for 2020 placed it at $2,746, a 16.18% decline from 2019, highlighting some minor variations in reporting, though both indicate a substantial contraction. This period was heavily impacted by intensified international sanctions and the global economic slowdown. However, 2021 saw a remarkable rebound. **Iran's GDP per capita** for 2021 was $4,335 USD, marking an impressive 45.04% increase from 2020. This substantial growth suggests a degree of economic resilience and perhaps an adaptation to the challenging environment, possibly driven by a recovery in oil prices and internal economic adjustments. The momentum continued into 2022, albeit at a slower pace. Iran's GDP per capita for 2022 was $4,405 USD, showing a modest 1.62% increase from 2021. This indicates a stabilization of the recovery, moving towards more sustainable growth rates after the sharp rebound. For 2023, the data shows continued, albeit slow, growth. According to the World Bank, GDP per capita (current US$) in Iran was reported at $4,466 USD in 2023. Another source indicates the latest value from 2023 as $4,465.64 USD, an increase from $4,405.09 USD. This slight increase suggests a continued, albeit challenging, path to economic improvement. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Iran was worth $404.63 billion USD in 2023, according to official data from the World Bank, though another figure states Iran's GDP for 2023 was $401.50 billion USD, a 2.88% decline from 2022. This discrepancy in overall GDP figures for 2023 (decline vs. slight increase in per capita) might be due to population changes or different data compilation methods, but the per capita figure generally shows a slight positive movement. Looking ahead to 2024, estimates suggest a further modest increase. The GDP per capita of Iran in 2024 was estimated at €4,094 or $4,430 USD, which is €290 or $315 USD higher than in 2023 (which was €3,804 or $4,115 USD). Another estimate for 2024 pegs the **GDP per capita in Iran** at $4,633 USD, compared to $4,347 USD in 2023. These projections, while still relatively low compared to global averages, indicate a cautious optimism for continued, albeit slow, economic expansion.Nominal vs. Purchasing Power Parity (PPP): A Deeper Dive
When discussing GDP per capita, it's crucial to differentiate between nominal values and those adjusted for Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). Nominal GDP per capita measures the economic output per person using current market exchange rates. While useful for international comparisons of economic size, it doesn't always reflect the actual purchasing power of individuals within a country, especially when exchange rates are volatile or heavily managed. Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) offers a more accurate picture of real living standards. PPP adjusts for differences in the cost of living and inflation rates between countries, allowing for a more meaningful comparison of economic well-being. It essentially asks: how much can a dollar buy in Iran compared to how much it can buy in the United States? Estimates by the World Bank for Iran's GDP per capita are available in nominal terms since 1960 and in PPP terms since 1990, at both current and constant prices, providing a comprehensive view.The Power of PPP in Iran
The latest value for Iran's GDP per capita, when adjusted by Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), was recorded at $15,912.03 USD in 2023. This marks an increase from $15,331 USD in a previous period. Another World Bank estimate for 2023, specifically "GDP per capita, PPP (current international $)", reports it at $17,660 USD. The difference between these PPP figures might stem from variations in the basket of goods used for comparison or the specific "international dollar" conversion method. Regardless, both figures are significantly higher than the nominal GDP per capita, illustrating that the cost of living in Iran is relatively lower, meaning a dollar goes further there than in many other parts of the world. In essence, the gross domestic product per capita, in Iran, when adjusted by purchasing power parity, is equivalent to 90 percent of the world's average. This is a substantial improvement compared to the nominal comparison, which we will discuss next.Iran GDP Per Capita in the Global Context
Placing Iran's GDP per capita within a global framework provides crucial context for understanding its economic standing. Comparisons to world averages, both nominal and PPP, reveal the challenges and relative strengths of the Iranian economy. In nominal terms, Iran's GDP per capita stands significantly below the global average. The latest value for Iran from 2023 is $4,465.64 USD. In comparison, the world average for 2023 is $19,958.31 USD, based on data from 185 countries. This means that the **GDP per capita in Iran** is equivalent to only about 45 percent of the world's average in nominal terms. This disparity highlights the impact of factors like sanctions, which affect Iran's ability to integrate fully into the global economy and realize its full potential based on its resources and population. However, the picture changes considerably when we look at Purchasing Power Parity (PPP). As mentioned, Iran's GDP per capita in PPP terms was $15,912 USD in 2023, or even $17,660 USD (current international $). In comparison, the world average for GDP per capita in PPP terms is $26,826 USD, based on data from 183 countries. This means that Iran's GDP per capita, when adjusted by purchasing power parity, is equivalent to approximately 90 percent of the world's average. This is a much more favorable comparison, suggesting that while Iranians may earn less in nominal terms, their money goes further domestically, allowing for a standard of living that is closer to the global average than nominal figures would suggest. This distinction is vital for a comprehensive understanding of the economic realities for the average Iranian.Factors Influencing Iran GDP Per Capita
The trajectory of **Iran's GDP per capita** is not merely a set of numbers; it's a reflection of complex interplay among various domestic and international factors. Understanding these influences is key to grasping the dynamics of the Iranian economy. One of the most significant factors is the **impact of international sanctions**. For decades, Iran has faced various forms of economic sanctions, primarily from the United States and its allies, largely due to its nuclear program and regional policies. These sanctions have severely restricted Iran's ability to sell its oil on international markets, access global financial systems, and import necessary goods and technologies. This directly impacts foreign investment, export revenues, and overall economic growth, consequently suppressing GDP per capita. **Oil prices and production levels** are another critical determinant. As a major oil producer, Iran's economy is heavily reliant on oil revenues. Fluctuations in global oil prices directly affect the nation's income, which in turn influences government spending, investment, and ultimately, the GDP per capita. Sanctions often target Iran's oil exports, further complicating this reliance. **Domestic economic policies and reforms** also play a crucial role. Government decisions regarding subsidies, taxation, privatization, and efforts to diversify the economy away from oil can have profound effects. Policies aimed at improving the business environment, fostering innovation, and controlling inflation are vital for sustainable growth. However, internal challenges such as high inflation, unemployment, and structural economic issues continue to pose hurdles. Finally, **population growth and demographics** are fundamental to the "per capita" calculation. While Iran's overall GDP might fluctuate, changes in its mid-year population can significantly alter the per capita figure. A rapidly growing population without commensurate economic growth can dilute the per capita income, even if the absolute GDP shows some increase. The absolute value of GDP in Iran rose by €26,222 million ($28,537 million) with respect to 2023, and the GDP per capita of Iran in 2024 was €4,094 ($4,430), €290 ($315) higher than in 2023. These figures demonstrate that while the overall economy might grow, the per capita improvement is a function of both GDP growth and population dynamics.Challenges and Outlook for Iran's Economic Future
Despite signs of resilience and periods of growth, Iran's economy, and consequently its **GDP per capita**, continues to face formidable challenges. The outlook remains complex, shaped by both internal reforms and external geopolitical pressures. The persistence of international sanctions is arguably the most significant hurdle. As long as these restrictions remain in place, Iran will struggle to fully leverage its economic potential, attract large-scale foreign investment, and integrate into the global financial system. This limits its ability to modernize industries, create jobs, and improve living standards for its citizens. The lack of access to critical technologies and markets can stifle innovation and productivity growth, which are essential for boosting GDP per capita. High inflation is another persistent problem in Iran. While not explicitly detailed in the per capita data, high inflation erodes purchasing power and creates economic uncertainty, discouraging long-term investment and savings. This directly impacts the real income and well-being of households, even if nominal GDP per capita figures show some increase. Structural economic issues, such as a large state-dominated sector, inefficiencies, and a challenging business environment, also hinder sustainable growth. Efforts to diversify the economy away from oil, promote the private sector, and improve governance are crucial for long-term stability and growth in **Iran's GDP per capita**. Looking ahead, Iran's economic future hinges on several factors: the potential for a breakthrough in nuclear negotiations that could lead to sanction relief, the government's commitment to meaningful economic reforms, and the stability of global oil markets. While recent data shows modest increases and resilience, achieving significant and sustained improvements in GDP per capita will require overcoming these deep-seated challenges. The average GDP per capita in Iran over the last decade (2014-2024) was approximately $4,451 USD, with 2024 estimated at $4,633 USD compared to $5,910 USD in 2014. This indicates that while there have been periods of recovery, the overall trend over the past decade has been one of struggle to regain previous highs.Conclusion: Navigating Iran's Economic Landscape
The journey of **Iran's GDP per capita** is a compelling testament to the nation's economic resilience amidst a landscape of considerable challenges. From historical highs in the 1970s to the sharp declines and subsequent recoveries of recent years, the data paints a picture of an economy constantly adapting. While nominal figures highlight the significant gap between Iran and the global average, the Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) data offers a more optimistic view, suggesting that the actual purchasing power of Iranians is closer to the world average than often perceived. Understanding these nuances is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the economic realities within Iran. The interplay of international sanctions, volatile oil markets, and domestic policies will continue to shape the trajectory of Iran's economic indicators. As Iran navigates its path forward, the evolution of its GDP per capita will remain a key metric for assessing its progress and the well-being of its population. What are your thoughts on Iran's economic trajectory? Share your insights in the comments below, or explore more of our articles on global economic trends and their impact on daily lives. Your engagement helps us foster a deeper understanding of these critical topics.- Unveiling Tommy Lee Jones Health Secret Exploring His Undisclosed Disease
- The 5 Golden Rules Of Kannada Cinema On Moviecom
- James Mcavoys Children A Glimpse Into The Family Of The Scottish Actor
- Sadie Mckenna Community Forum Connect Share And Learn
- The Renowned Actor Michael Kitchen A Master Of Stage And Screen
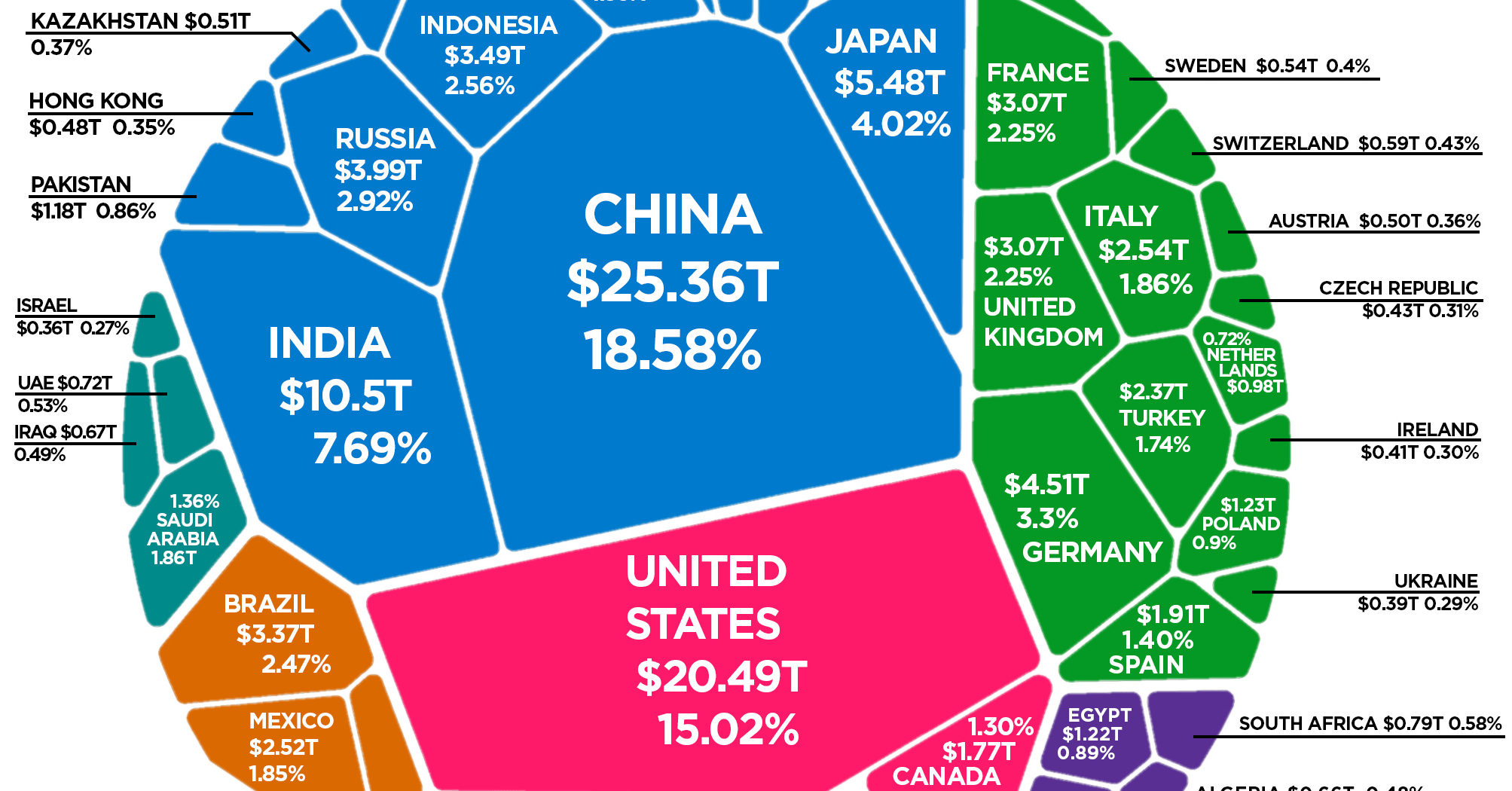
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country