Understanding The IRR: Iran's Official Currency Explained
The Iranian Rial (IRR) is the official currency of Iran, a subject of immense interest given the nation's unique economic landscape and geopolitical position. For anyone looking to understand Iran's financial system, whether for travel, business, or general knowledge, grasping the intricacies of the IRR is fundamental. This comprehensive guide delves into the history, structure, challenges, and future prospects of Iran's currency, offering a clear and accessible overview.
The journey of the Iranian Rial has been marked by significant historical shifts, economic pressures, and ongoing discussions about its fundamental value and future. From its historical introduction to its current status as the legal tender of the Islamic Republic of Iran, the IRR plays a central role in the daily lives of millions and in the country's interactions with the global economy. Understanding its nuances, including its relationship with the Toman and its exchange rates, is crucial for a complete picture.
Table of Contents
- What is the Iranian Rial (IRR)?
- A Journey Through Time: The History of the Iranian Rial
- Understanding the Denominations: Rial vs. Dinar vs. Toman
- The IRR in the Global Economy: Exchange Rates and Challenges
- Navigating Currency Exchange: Tips for Travelers and Investors
- The Future of the Iranian Rial: Tomanization and Economic Reforms
- Where to Buy Iranian Rial (IRR)
- Conclusion: The Enduring Story of the Iranian Rial
What is the Iranian Rial (IRR)?
The Iranian Rial (IRR) is the official currency of the Islamic Republic of Iran. Often referred to as "Rl" (singular) and "rls" (plural) or "ir" in Latin, its currency code is IRR, and its symbol is ﷼. While it is theoretically subdivided into 100 dinars, the dinar is not practically used due to the rial's significantly low purchasing power. This means that despite the official subdivision, transactions are conducted solely in rials, or more commonly, in Tomans, a unit that simplifies calculations for everyday use. Our currency rankings consistently show that the most popular Iranian Rial exchange rate is the IRR to USD rate, reflecting the global interest in understanding its value against major international currencies.A Journey Through Time: The History of the Iranian Rial
The history of the Iranian Rial is a fascinating narrative of economic evolution, political shifts, and currency reforms. It underscores the resilience and adaptability of Iran's financial system in the face of various internal and external pressures.Early Introduction and Disappearance
The Iranian Rial was first introduced in 1798 as a coin, initially valued at 1,250 dinars. This early iteration of the rial, however, did not have a continuous presence in Iran's monetary system. By 1825, the rial had ceased to be in circulation, replaced by the qiran. The qiran served as the primary currency for nearly a century, representing a significant period in Iran's economic history before the rial's eventual re-emergence. This initial phase highlights the dynamic nature of currency in historical contexts, where different units of value rise and fall based on economic needs and political decisions.Reintroduction and Modern Era
The rial made its return to Iran's financial landscape much later, in 1923. Upon its reintroduction, it was traded at a rate of 1 rial = 1 qiran, establishing a direct link to the preceding currency. This re-establishment marked the beginning of the modern era for the Iranian Rial, solidifying its position as the official currency. Since then, the IRR has been at the heart of Iran's economy, navigating through various periods of growth, stability, and significant challenges. A notable development occurred in 2012 when the government launched a foreign exchange centre. This initiative aimed to provide importers of certain basic goods with foreign exchange at a rate approximately 2% cheaper than the open market rate. Such measures illustrate the government's efforts to manage the currency's value and stabilize the economy, particularly in sectors deemed critical for public welfare. Despite its historical significance, the IRR continues to face considerable challenges, including economic sanctions, political instability, and ongoing discussions about its potential replacement with the Toman. These factors contribute to the complexity and volatility often associated with the Iranian Rial.Understanding the Denominations: Rial vs. Dinar vs. Toman
For anyone unfamiliar with the Iranian currency, the distinction between the Rial, Dinar, and Toman can be confusing. While the Rial is the official legal currency, the Toman is the unit most commonly used in everyday transactions, and the Dinar is largely obsolete in practical terms.The Dinar Dilemma
The Iranian Rial is officially subdivided into 100 dinars. However, due to the rial's extremely low purchasing power, dinar denominations of the Iranian currency are not typically used. This means you will not encounter coins or banknotes denominated in dinars in daily life. The concept of the dinar as a subdivision exists primarily in official definitions, but its practical application has long ceased. This situation is a clear indicator of the significant depreciation the rial has experienced over time, rendering its smaller theoretical units practically worthless for transactional purposes.The Toman's Practicality
Sometimes referred to as Toman, there is a significant difference in value between the two, which is crucial to understand. The Toman is not an official currency unit but rather a commonly used denomination where 1 Toman equals 10 rials. This means that when Iranians discuss prices or exchange money, they almost always refer to Tomans. For example, 100,000 Iranian rials (IRR) is equivalent to 10,000 Tomans, reflecting a difference of one zero (not three zeros as mistakenly stated in some data, it's 1 Toman = 10 Rials, so 100,000 Rials = 10,000 Tomans). This practical convention simplifies large numbers and makes transactions more manageable for the general public. It's vital for visitors and those dealing with the Iranian economy to remember this conversion: if a price is quoted in Tomans, add a zero to get the Rial value, or conversely, remove a zero from a Rial value to get the Toman equivalent. This dual system, with the official Rial and the practical Toman, is a unique characteristic of the Iranian currency landscape.The IRR in the Global Economy: Exchange Rates and Challenges
The Iranian Rial's position in the global economy is largely defined by its exchange rates against major currencies and the unique challenges it faces, particularly economic sanctions and political instability.Key Exchange Rates: IRR to USD and Others
As previously mentioned, the most popular Iranian Rial exchange rate is the IRR to USD rate. This rate is a critical indicator of the rial's strength and the health of the Iranian economy. Historical data shows significant fluctuations. For instance, in the last 10 years, the highest rate from Iranian Rials to US Dollars was on January 1, 2017, when each Iranian Rial was worth 0.00003325 US dollars. This historical peak highlights periods where the rial held relatively more value against the dollar. Beyond the USD, the Iranian Rial is also exchanged against other currencies. For example, the cost of 1 Iranian Rial in Pakistani Rupees today is approximately ₨0.01, according to "open exchange rates," with the exchange rate remaining unchanged recently. Similarly, one can learn the value of 1 Indian Rupee (INR) in Iranian Rials (IRR) today using online currency converters. These rates, along with charts and tables showing the dynamics of exchange rate changes for a day, week, month, and year, are readily available through various online tools. The IRR and USD can be traded 24x5, starting from the time markets open on Monday mornings in Sydney until they close on Fridays at 5 PM in New York, reflecting the continuous nature of global forex markets.Factors Influencing the IRR's Value
The value of the Iranian Rial is heavily influenced by a confluence of factors, primarily economic sanctions, political instability, and internal economic policies. Economic sanctions imposed by international bodies and individual countries have severely restricted Iran's access to global financial markets and its ability to export oil, a primary source of foreign currency. This limitation of foreign exchange inflow puts immense downward pressure on the rial's value. Political instability, both within Iran and in the broader Middle East, also contributes to currency volatility. Uncertainty discourages foreign investment and can lead to capital flight, further weakening the IRR. Domestically, government policies, including efforts to control inflation, manage foreign exchange reserves, and implement economic reforms, play a crucial role. The ongoing discussions of replacing the rial with the toman are themselves a reflection of the challenges the currency faces and an attempt to re-anchor public confidence in the monetary system by simplifying its value.Navigating Currency Exchange: Tips for Travelers and Investors
For those looking to convert currencies, especially to or from the Iranian Rial, understanding the process and available tools is essential. Online currency converters provide a straightforward way to get real-time rates and perform conversions. For example, to convert US Dollars to Iranian Rial, one simply types in the amount desired, selects USD in the first dropdown as the currency to convert from, and IRR in the second dropdown as the currency to convert to. This allows users to quickly learn the value of 1 United States Dollar (USD) in Iranian Rials (IRR) today or convert 1 dollar to rials with an online currency converter. Similarly, to convert 1 Rupee to Rials, the same process applies. These tools also offer Iranian Rial rates, charts, and an IRR currency converter, providing insights into historical changes and current values. When sending money to or from Iran, it is advisable to compare exchange rates offered by various currency transfer providers to ensure the best possible rate. This currency rates table lets you compare an amount in Iranian Rial to all other currencies, aiding in informed financial decisions. It is important to note that due to the unique economic situation, official exchange rates might differ significantly from open market rates, and access to foreign currency within Iran can be restricted for non-essential purposes.The Future of the Iranian Rial: Tomanization and Economic Reforms
The future of the Iranian Rial is a topic of significant debate and policy consideration within Iran. The most prominent discussion revolves around the long-proposed "tomanization" of the currency. This plan involves officially redenominating the currency, effectively removing four zeros from the rial's value and making the Toman the new official currency unit. This move aims to simplify financial transactions, reduce the psychological impact of large nominal values, and potentially restore some confidence in the national currency. For instance, what is currently 100,000 Iranian Rials would officially become 10 Tomans. While the exact timeline for this transition remains fluid, the intent is clear: to streamline the monetary system and address the practical difficulties posed by the rial's low value. Beyond redenomination, the future of the IRR, or its successor the Toman, will heavily depend on broader economic reforms, the lifting of international sanctions, and the fostering of greater economic stability. Efforts to diversify the economy, attract foreign investment, and manage inflation will be crucial in determining the long-term strength and stability of Iran's currency. The success of these reforms will dictate whether the Iranian currency can achieve greater stability and integration into the global financial system.Where to Buy Iranian Rial (IRR)
For individuals interested in purchasing Iranian Rial (Toman), there are specific avenues available, although they might differ from typical currency exchange processes due to international sanctions and banking restrictions. Some specialized dealers and online platforms offer the sale of Iranian Rial in various denominations. For instance, some vendors claim to sell all denominations of IRR, including the 500k and 100k, the one million and two million IRR in uncirculated consecutive serial numbers. These services often cater to collectors, researchers, or individuals with specific needs for physical Iranian currency. It's important for potential buyers to exercise caution and ensure they are dealing with reputable sources, especially when purchasing currency online. Some platforms offer free shipping on Iranian currency orders and claim to sell Iranian Rial worldwide, allowing individuals to purchase Iranian Rial with confidence. However, due to the complexities surrounding the Iranian financial system, it's always advisable to verify the legitimacy and reliability of such services and to be aware of any legal or logistical restrictions that might apply to the import or export of Iranian currency in one's specific jurisdiction. For travelers, exchanging currency upon arrival in Iran at official exchange bureaus or banks is generally the most common and recommended method.Conclusion: The Enduring Story of the Iranian Rial
The Iranian Rial (IRR) is more than just a medium of exchange; it is a reflection of Iran's rich history, its economic resilience, and the challenges it continues to navigate on the global stage. From its reintroduction in 1923 to its current status as the official currency of the Islamic Republic of Iran, the IRR has undergone significant transformations. Its unique characteristics, such as the practical use of the Toman and the theoretical subdivision into dinars, highlight the adaptations necessary in a dynamic economic environment. Despite facing considerable headwinds from economic sanctions and political instability, the Iranian Rial remains central to the nation's economy. The ongoing discussions about its redenomination to the Toman underscore a persistent effort to stabilize and modernize Iran's monetary system. For anyone seeking to understand Iran, whether as a traveler, an investor, or simply an observer of global economics, comprehending the intricacies of the Iranian Rial is indispensable. We hope this comprehensive overview has provided valuable insights into the fascinating world of Iran's currency. What are your thoughts on the future of the Iranian Rial? Share your perspectives in the comments below, or explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of global currencies and economies.- Uproar Of Scandal In The Year Of 2024 A Deeper Exploration
- The Unveiling Of Rebecca Vikernes Controversial Figure Unmasked
- Download The Latest 2024 Kannada Movies For Free
- An Unforgettable Journey With Rising Star Leah Sava Jeffries
- The Last Glimpse A Heartbreaking Farewell To Amy Winehouse
What Is Internal Rate of Return (IRR)? – 365 Financial Analyst

Internal rate of return (IRR) - What is, calculation and examples
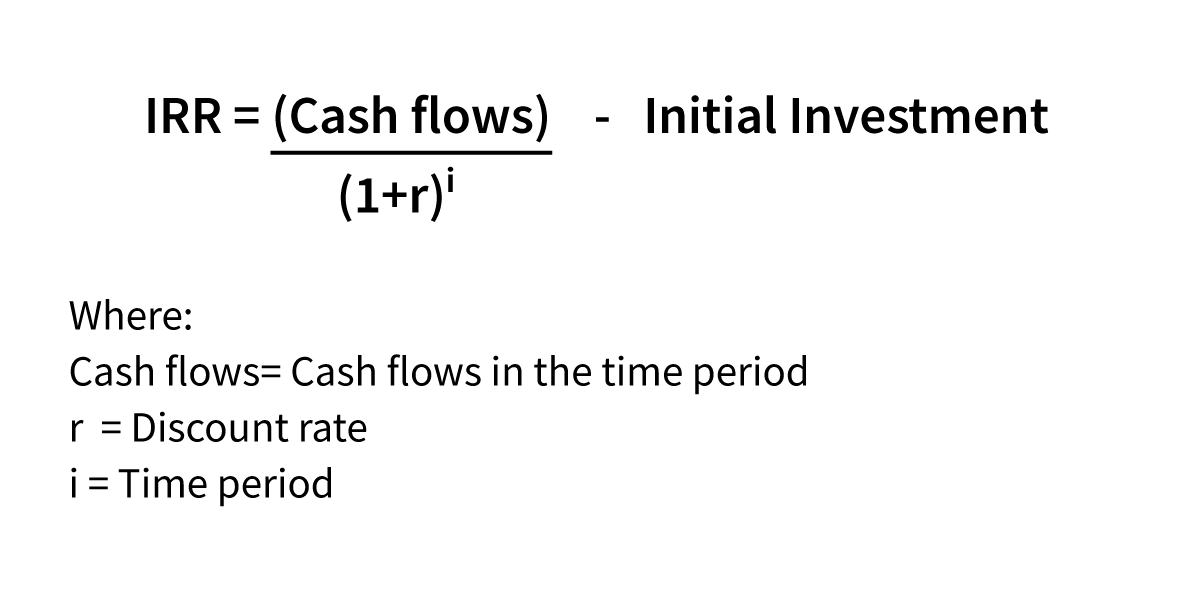
Internal Rate of Return - Meaning, Formula and Usage