Iran's Oil Output: Unpacking Production & Global Impact
When we talk about the global energy landscape, few nations hold as much strategic importance and intrigue as Iran. A founding member of OPEC and a country blessed with vast hydrocarbon wealth, the question of "how much oil does Iran produce" is not merely a statistical inquiry but a crucial indicator of geopolitical shifts, economic resilience, and the intricate balance of supply and demand in the international market. Understanding Iran's oil production is essential for anyone tracking global energy trends, as its output directly influences crude prices, regional stability, and the broader economic health of both producing and consuming nations.
Iran's journey as an oil producer is a saga spanning over a century, marked by periods of booming prosperity, revolutionary change, and the persistent challenges posed by international sanctions. Despite these hurdles, Iran remains a formidable force, consistently demonstrating its capacity to rebound and maintain its position among the world's top oil producers. This article delves deep into the specifics of Iran's oil production, exploring its historical trajectory, current output levels, the factors that shape its industry, and what the future might hold for this pivotal energy player.
Table of Contents
- A Century of Oil: Iran's Rich Hydrocarbon Heritage
- Unveiling Iran's Vast Oil Reserves
- How Much Oil Does Iran Produce Today? Navigating Current Figures
- The Export Landscape: Iran's Oil Reaching Global Markets
- Factors Influencing Iran's Oil Production
- The Future Outlook: What Lies Ahead for Iran's Oil Industry?
- Iran's Oil Production: A Vital Global Energy Player
A Century of Oil: Iran's Rich Hydrocarbon Heritage
Iran's relationship with oil is as old as the modern oil industry itself. With more than a century of history in exploration and production, the nation has been a significant player on the global energy stage for generations. This long and storied past is fundamental to understanding its current capabilities and future potential.
- Shag Carpet Installation Your Ultimate Guide To Easy Home Upgrades
- Mark Davis Wife Unveiling Her Age And Relationship
- Rowoons Latest Buzz Breaking Entertainment News
- The Legendary Teddy Riley An Rb Trailblazer
- Kevin Jrs Wife Uncovering The Identity Behind The Mystery
Deep Roots: Early Discoveries and Development
The dawn of Iran's oil industry traces back to 1908, marking the beginning of a transformative era for the nation. From its outset, the country quickly established itself as a major source of crude oil. Over nearly a century, from 1908 to the end of 2007, Iran had already produced an astonishing 61 billion barrels of oil. This figure alone underscores the sheer scale of its hydrocarbon wealth and its enduring contribution to global energy supply. The expertise accumulated over these decades, from exploration techniques to production methodologies, forms the backbone of Iran's oil sector, enabling it to navigate complex geological challenges and maintain output even under difficult circumstances.
The Golden Era: Peak Production in the 1970s
The 1970s represented the zenith of Iran's oil production, a period often referred to as its "golden era." During this decade, Iran's output reached unprecedented levels, cementing its position as one of the world's leading oil exporters. According to OPEC data, Iran’s oil production was at its peak in the 1970s, with a record output of 6 million barrels per day (bpd) in 1974. To put this into perspective, that amounted to more than 10% of the world's total oil output at the time. This period of immense production not only fueled Iran's economic development but also gave it significant leverage in global energy politics. The legacy of this era, characterized by massive infrastructure development and a highly skilled workforce, continues to influence Iran's oil industry today, even as it strives to recapture some of that past glory amidst contemporary challenges.
Unveiling Iran's Vast Oil Reserves
Beyond its historical production, Iran's future potential is intrinsically linked to its immense proven oil reserves. The nation holds some of the world’s largest deposits of proved oil, a fact that underpins its long-term significance in the global energy market. These reserves are not just numbers; they represent a strategic asset that ensures Iran's continued relevance for decades to come, regardless of short-term production fluctuations.
- Jzsef Barsi The Tragic Story Of A Young Hollywood Star
- Discover Megnutts Leaks Unveiling The Truth Behind The Controversies
- Lou Ferrigno Jr Bodybuilding Legacy Acting Success
- Josephine Pintor An Artists Journey Discover Her Unique Style
- Ultimate Guide To Xnxnxn Beyond The Basics
As of 2016, Iran held an impressive 157,530,000,000 barrels of proven oil reserves. This colossal figure ranks Iran as the #4 country in the world for oil reserves, accounting for approximately 9.54% of the world’s total proven oil reserves, which stood at 1,650,585,140,000 barrels at that time. Such vast reserves mean that Iran has the capacity to sustain its production for a considerable period. In fact, as of 2016, Iran’s proven reserves were equivalent to 239.2 times its annual consumption levels, indicating a remarkable longevity for its oil resources. This substantial reserve base is a key factor in understanding "how much oil does Iran produce" and, more importantly, how much it can produce in the future, given the right investment and geopolitical conditions. These figures highlight Iran's inherent strength as a major energy power, a strength that persists despite the various pressures it faces on its current output.
How Much Oil Does Iran Produce Today? Navigating Current Figures
The question of "how much oil does Iran produce" is dynamic, with figures fluctuating based on a variety of internal and external factors. Unlike the relatively stable reserve numbers, production data offers a snapshot of Iran's current operational capacity and its response to market demands and geopolitical pressures. It's a complex picture, with different reports offering slightly varied but consistently insightful data points.
Recent Production Trends and Fluctuations
Iran's oil production data is updated monthly, reflecting the fluid nature of the industry. According to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) latest oil market report, released in October, Iran produced 3.14 million barrels of crude oil per day, excluding condensates. This figure provides a recent benchmark for its output. Looking at more granular monthly data, production was reported at 3,280,000 barrels per day in January 2025, which marked a slight decrease from the previous month's number of 3,293,000 barrels per day for December 2024. Further demonstrating these short-term shifts, crude oil production in Iran decreased to 3303 bbl/d/1k in May from 3328 bbl/d/1k in April of 2025.
Despite these minor month-to-month dips, the broader trend indicates a significant recovery from earlier lows. Estimates suggest that oil production in Iran has increased around 75 percent to about 3.4 million barrels a day from depressed 2020 levels. This rebound is a testament to Iran's resilience and its ability to ramp up production when conditions allow. For instance, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) reported that Iran’s oil production in February rose from the previous month's level of 3.274 million bpd, further reinforcing the upward trajectory observed in recent years. The latest value from 2023 stands at 3625.15 thousand barrels per day, marking a notable increase from 3293.4 thousand barrels per day in 2022, showcasing a consistent effort to boost output year-over-year.
Historical Averages and Global Comparison
To fully grasp "how much oil does Iran produce," it's helpful to contextualize its current output against its historical performance and global averages. Historically, the average for Iran from 1973 to 2023 is 3580.35 thousand barrels per day, a figure that includes the highs of the 1970s and the lows of various sanction regimes. More recently, the average production from January 2002 to January 2025 has been around 3,521,000 barrels per day. This long-term average demonstrates Iran's consistent, albeit fluctuating, role as a major producer.
When comparing Iran's output to the rest of the world, its position remains significant. As of 2016, Iran produced 4,376,194 barrels per day of oil, ranking #7 in the world among countries by oil production. In comparison, the world average is a much smaller 429.63 thousand barrels per day, based on data from 190 countries. This stark contrast underscores Iran's disproportionately large contribution to global oil supply. While its current production levels are below its historical peak of 6 million bpd in 1974, they still place Iran among the elite group of nations that significantly influence the global energy market. The country produces every year an amount equivalent to 1.01% of its total proven reserves (as of 2016), indicating a sustainable extraction rate relative to its vast underground wealth.
The Export Landscape: Iran's Oil Reaching Global Markets
Production figures tell only half the story; the other crucial half lies in exports. For Iran, the ability to export its crude oil is paramount, as it directly translates into foreign currency reserves and economic stability. The export landscape for Iran is heavily influenced by geopolitical factors, particularly international sanctions, but recent trends show a remarkable resurgence.
Iranian oil exports have increased more than threefold over the past three years. This significant surge is a direct consequence of relaxed U.S. sanctions enforcement and increased Chinese demand for heavily discounted crude. According to Kpler trade intelligence firm’s tanker tracking data, Iran’s crude oil and gas condensate exports reached 1.812 million barrels per day (mb/d) together in October, the highest since 2019 and about 370,000 b/d more than in September 2023. This demonstrates a robust recovery in its ability to move oil to international buyers.
Further illustrating this upward trend, Iran exported 141.7 million barrels of oil during the first quarter of 2024, representing a substantial 28 percent increase over the same period last year. These increased oil exports are vital for Tehran, as they enhance its currency reserves and enable the government to fund various domestic and international initiatives. The strong demand, particularly from China, for Iran's heavily discounted crude, has provided a critical lifeline, allowing Iran to monetize a significant portion of "how much oil does Iran produce" despite ongoing sanctions. This dynamic interplay between production capacity, export channels, and global demand is central to Iran's economic resilience.
Factors Influencing Iran's Oil Production
Understanding "how much oil does Iran produce" requires an examination of the multifaceted factors that constantly shape its output. These influences range from geological realities to complex geopolitical dynamics, all of which contribute to the volatility and resilience of Iran's oil industry.
- International Sanctions: Undoubtedly, the most significant external factor impacting Iran's oil production and exports are international sanctions, primarily those imposed by the United States. These sanctions target Iran's oil sales, financial transactions, and access to technology, severely limiting its ability to invest in infrastructure, attract foreign partners, and sell its crude on the open market. The recent increase in exports is attributed to relaxed enforcement of these sanctions rather than their complete removal, highlighting their persistent influence. When sanctions are strictly enforced, Iran's production and export capabilities are severely hampered; when enforcement eases, the industry demonstrates a remarkable ability to rebound quickly.
- Aging Infrastructure and Production Decline Rates: Decades of underinvestment, partly due to sanctions and partly due to internal priorities, have led to aging oil fields and infrastructure. This poses a significant challenge to maintaining and increasing production. As early as 2006, the rate of production decline was reported at 8 percent for Iran's existing onshore oil fields (which furnish the majority of oil output) and 10 percent for existing offshore fields. Counteracting these natural decline rates requires substantial capital investment, advanced technology, and expertise, much of which has been restricted by sanctions. Without continuous investment in enhanced oil recovery techniques and the development of new fields, maintaining current production levels, let alone increasing them, becomes increasingly difficult.
- Technological Access and Foreign Investment: Modern oil production, especially from mature fields, relies heavily on cutting-edge technology and significant foreign investment. Sanctions have largely cut Iran off from major international oil companies (IOCs) and their technological prowess and capital. While Iran has developed domestic capabilities, they often cannot fully compensate for the advanced technologies and vast financial resources that IOCs bring. Agreements, such as a more modest yet important agreement signed with India to explore and produce oil and natural gas in southern Iran, indicate a willingness to seek partnerships where possible, but larger-scale collaborations remain constrained.
- Domestic Consumption and Energy Policy: While less impactful on export figures, domestic energy consumption patterns and government policies also play a role. Iran is a significant energy consumer itself, and meeting internal demand influences the volume available for export. Government policies regarding subsidies, energy efficiency, and the development of alternative energy sources can indirectly affect the pressure on crude oil production.
These interwoven factors create a complex operational environment for Iran's oil industry, where geopolitical maneuvering, technological limitations, and economic imperatives constantly shape "how much oil does Iran produce" and how much it can sell to the world.
The Future Outlook: What Lies Ahead for Iran's Oil Industry?
The future of "how much oil does Iran produce" is a subject of intense speculation, deeply intertwined with geopolitical developments, particularly the fate of international sanctions. Despite the challenges, Iran's fundamental strengths – its massive reserves and a century of industry experience – position it for potential growth.
If sanctions were to be significantly eased or lifted, Iran possesses the capacity for a rapid increase in production. Its existing infrastructure, while aging, could be quickly revitalized with an influx of foreign investment and technology. Major international oil companies, eager to access Iran's vast reserves, would likely rush in, bringing the capital and expertise needed to boost output from both existing fields and undeveloped ones. This could potentially see Iran returning closer to its historical production highs, significantly impacting global oil supply and prices.
However, even without a complete lifting of sanctions, Iran has demonstrated its ability to adapt. The increased exports due to relaxed enforcement and strong demand from certain buyers indicate a resilient, if constrained, pathway forward. Continued focus on internal technological development, smaller-scale partnerships, and efficient management of existing assets will be crucial. The challenge of maintaining aging fields and managing natural decline rates will persist, requiring continuous innovation and investment. Ultimately, while the full potential of Iran's oil industry remains largely dependent on external political decisions, its inherent resource wealth ensures it will remain a formidable and relevant player in the global energy market for the foreseeable future.
Iran's Oil Production: A Vital Global Energy Player
In conclusion, the question of "how much oil does Iran produce" reveals a narrative of immense potential, historical significance, and contemporary resilience. Iran's position as a global energy player is undeniable, anchored by its vast proven oil reserves, which rank among the largest in the world. From its pioneering days in the early 20th century to its peak output in the 1970s, and through the complex challenges of the modern era, Iran has consistently demonstrated its capacity to contribute substantially to the world's energy needs.
While current production figures fluctuate, influenced heavily by geopolitical factors and the state of international sanctions, recent data points to a significant rebound from earlier lows. Iran continues to produce millions of barrels per day, and its exports have shown remarkable growth, especially towards Asian markets, bolstering its economic stability. The inherent challenges of aging infrastructure and the need for continuous investment remain, yet the country's deep expertise and strategic importance ensure its enduring relevance.
Understanding Iran's oil production is more than just tracking numbers; it's about comprehending a critical component of global energy security, geopolitical dynamics, and the economic well-being of a nation with profound historical ties to the oil industry. Iran's journey as an oil producer is far from over, and its future trajectory will undoubtedly continue to shape the contours of the international energy landscape.
What are your thoughts on Iran's role in the global energy market? Share your insights in the comments below! If you found this analysis insightful, consider sharing it with others interested in global energy dynamics or exploring more of our articles on the subject.
- Sadie Mckenna Community Forum Connect Share And Learn
- The Ultimate Guide To Traylor Howard Biography Movies And Awards
- Pinay Flix Stream And Download The Best Pinay Movies And Tv Shows
- The Extraordinary Life And Legacy Of Rowena Miller
- Is Michael Steeles Wife White Yes Or No An Indepth Look

How Much Oil Does Iran Produce? - Oil Markets Daily (NYSEARCA:USO

Infographic: How much oil does Russia produce? | Infographic News
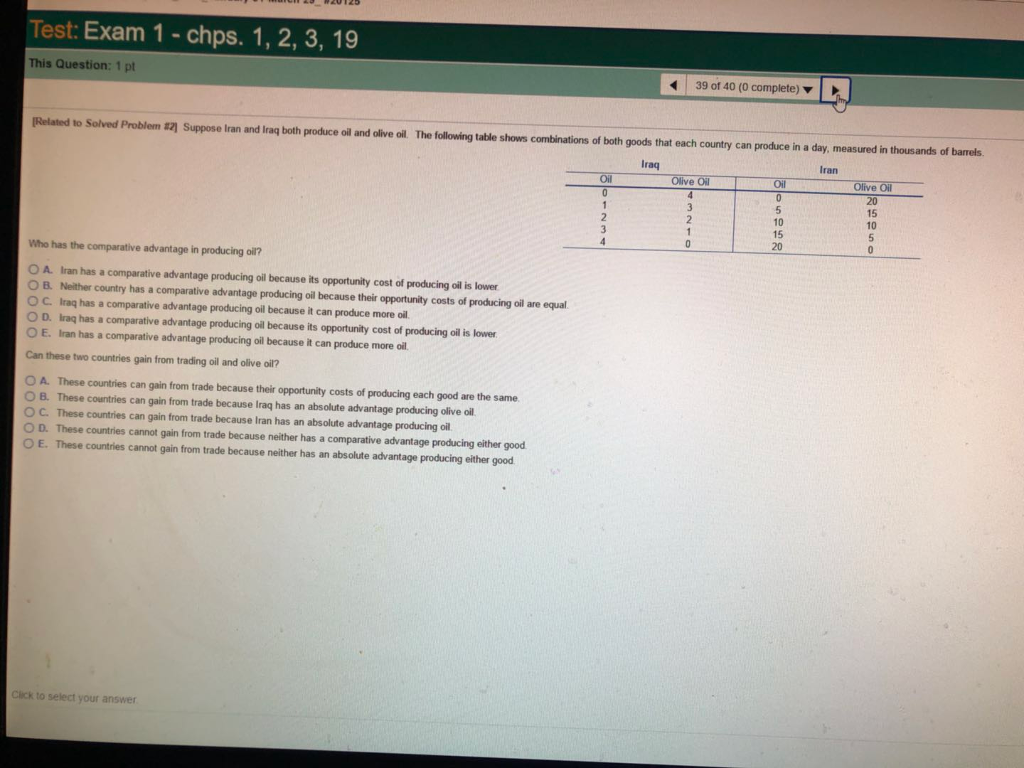
(Solved) - 12 Suppose Iran and Iraq both produce oil and olive oil